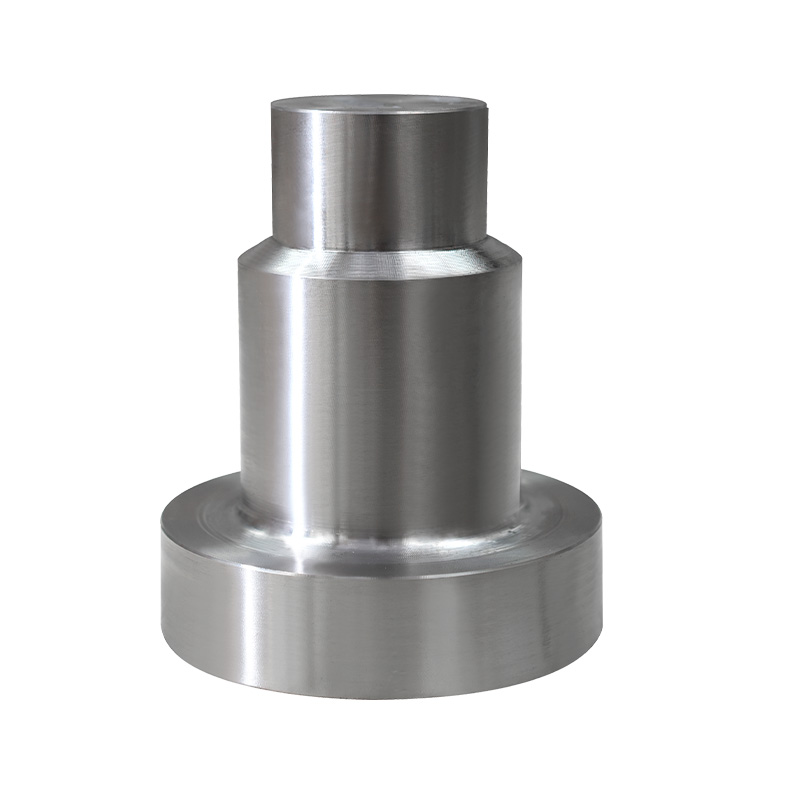
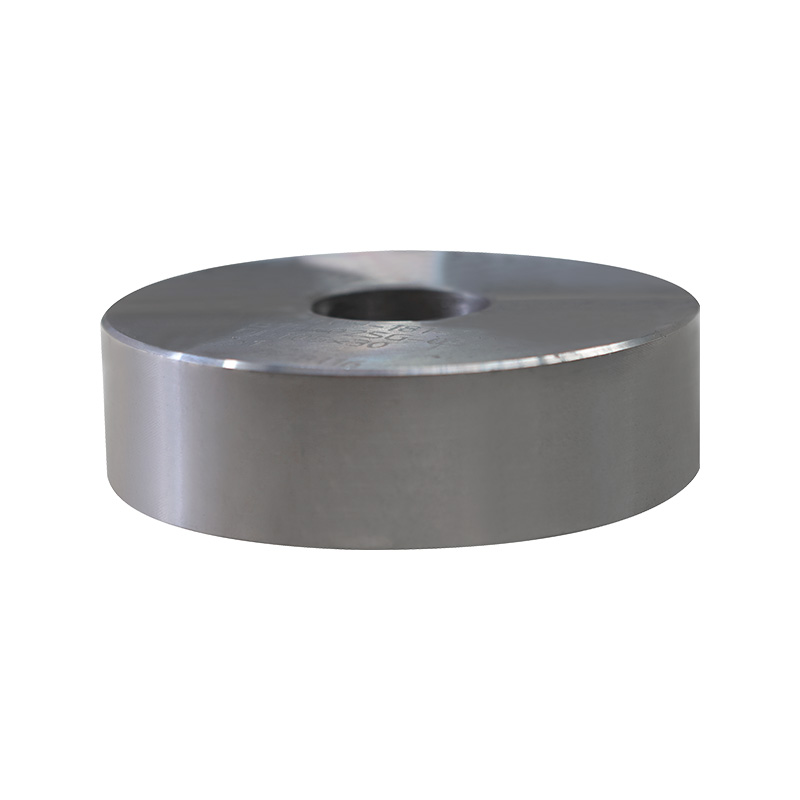
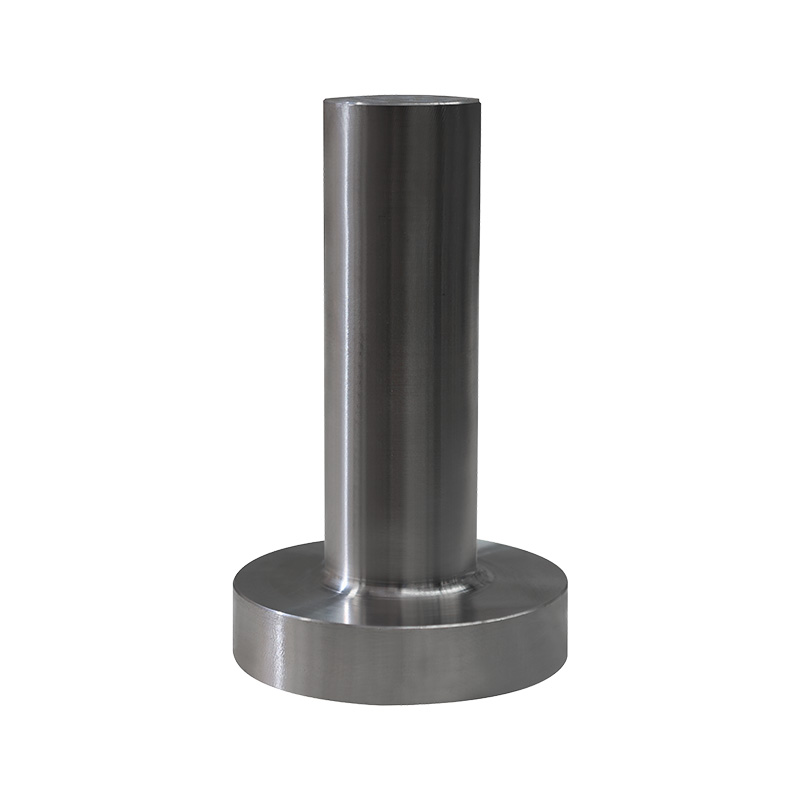
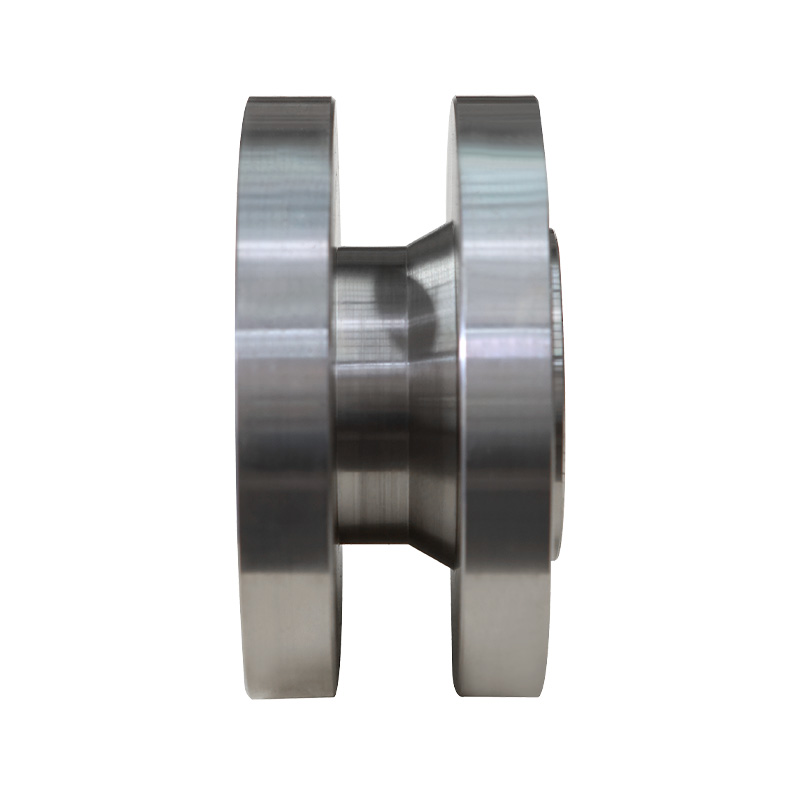
Alloy forging is the process of shaping alloy steel into specific forms using a "hot working" method. This not only changes the shape but also makes the metal stronger and more ductile through powerful compression.
The following is a detailed introduction to this process and product:
Content
● What is Alloy Forging?
Heating and Reshaping: Just like kneading clay before shaping it, alloy forging typically involves heating the metal block to a very high temperature to make it more malleable.
Powerful Compression: Once the metal softens, workers use massive machines (such as forging presses or large hammers) to repeatedly strike or powerfully compress it.
Internal "Degassing": During this process, any small pores or loose areas that may exist within the metal are completely compressed, resulting in an extremely dense structure.
● Why specifically mention Alloy Steel forgings?
Double the Performance: Ordinary steel is already strong after forging, but alloy steel forgings, because they contain "powerful ingredients" like chromium and nickel, and are further compressed during forging, achieve an astonishing level of strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Fibrous Structure: Forging causes the metal's internal particles (professionally called grains) to align neatly along the direction of the shape. This is similar to the grain of wood; wood is less likely to break when stressed along the grain. Alloy steel forgings therefore possess excellent impact resistance.
Long-lasting Durability: Parts produced by this process are much stronger than those directly cast from molds (castings), are less prone to cracking, and have a longer service life.
● Where is it used?
Due to the outstanding performance of alloy steel forgings, they are typically found in high-stress applications:
Critical Automotive Parts: For example, the axles connecting the wheels and the crankshafts in engines. These parts rotate and bear force at high speeds every day, so forged parts are essential for reliability.
Heavy Machinery: The "teeth" and joints of excavators and bulldozers that directly come into contact with rocks often use alloy steel materials. Aerospace and Energy: In critical and harsh environments such as aircraft landing gear and large valves in power plants, alloy forgings are almost exclusively used.


 英语
英语 德语
德语 阿拉伯语
阿拉伯语